Purpose
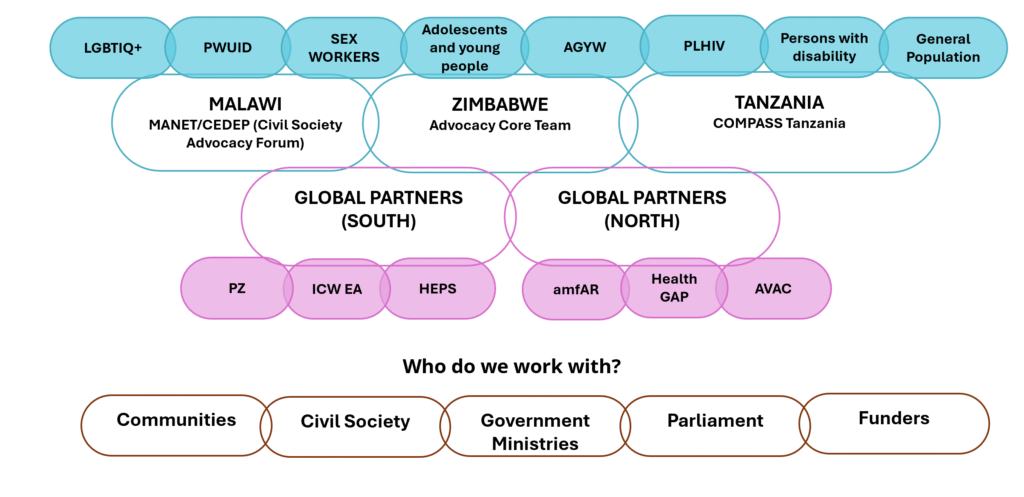
The Coalition to build Momentum, Power, Activism, Strategy & Solidarity in Africa (COMPASS Africa) is an audacious, data-informed transnational civil society coalition established in 2017 to strengthen the community-centred HIV response in Malawi, Tanzania, and Zimbabwe. Anchored by country-based coalitions and working in collaboration with regional and global partners in Africa and the United States, COMPASS combines grassroots leadership with seasoned advocacy expertise to shape national, regional, and global HIV responses. At its core, COMPASS is driven by community-led organizations, led by adolescents and young people (including AGYW), people living with HIV, key populations, and persons with disabilities. Their leadership ensures that the HIV response is not only effective but also equitable, inclusive, and sustainable.
For almost a decade, COMPASS has harnessed evidence and lived experience to drive strategic, collaborative advocacy that dismantles barriers, strengthens accountability, and secures community priorities within HIV and health responses. Through this coalition-based approach, COMPASS has helped shape policy, influence funding, and safeguard rights, contributing to a comprehensive HIV response that drives down new infections and AIDS-related deaths.
Who We Are
Pangaea Zimbabwe,as Prime and Secretariat of COMPASS Africa
Prime and Secretariat Role
Serves as liaison between the coalition and funder.
Manages fiduciary sub-granting to ensure transparency and accountability.
Provides Organisational Development Support, focusing on:
Grant and financial management.
Institutional capacity strengthening in key domains.
Equips partners with tools and systems to sustain their work and influence.
Internal Communications
Ensures effective communication at every level:
One-on-one with partners.
Within country coalitions.
Across regional thematic working groups.
With global partners and the wider coalition.
Facilitates open, consistent, and inclusive dialogue.
Strengthens internal collaboration and shared purpose.
Coalition Health and Governance
Safeguards COMPASS’s vision and mission while adapting to evolving contexts.
Maintains partner alignment and commitment.
Facilitates decision-making and conflict resolution.
Responds to emerging coalition issues.
Nurtures partnerships (South-South, South-North, in-country).
Aligns four thematic working groups to coalition-wide outcomes.
Strengthening Country Coalitions
Supports ACT Zimbabwe, CSAF Malawi, and COMPASS Tanzania.
Reinforces partner agency and autonomy.
Ensures country coalitions remain strong and central to the movement.
Safeguards the foundation and long-term impact of COMPASS.
Program Support and MERL Hub
Provides strategic and technical support to partners.
Convenes strategy labs using the Landscape Analysis for Campaign Planning Toolkit for evidence-based advocacy.
Offers real-time tactical planning support during implementation.
Measures advocacy impact using:
COMPASS Campaign Advocacy Assessment Tool (C-CAAT) – evaluates significance, influenceability, and durability of outcomes.
Simple Participatory Assessment of Real Change (SPARC) – captures advocacy impact from community and partner perspectives.
Provides a holistic view of measurable outcomes and lived experiences of change.
Leads learning processes through:
Case studies on best practices.
Insights into coalition governance.
Documentation of lessons for stronger future advocacy.

Coalition Focus Areas
COMPASS Africa’s coalition work is centered on the following strategic focus areas to advance equitable HIV and health outcomes.
Structural Barriers to Access
Outdated, restrictive, or under-implemented laws and policies create obstacles to equitable HIV and health service access.
Marginalized communities continue to face disproportionate impacts from these barriers.
Chronic Domestic Underfunding of HIV and Health
Heavy reliance on external donors (PEPFAR, Global Fund) threatens sustainability.
Government contributions remain below WHO-recommended per capita spending and the 5% GDP allocation benchmark.
Community Inclusion in Official Development Assistance (ODA)
Community voices are often sidelined in setting ODA priorities.
COMPASS actively involves communities in the governance, priority-setting, and accountability of ODA investments, focusing on PEPFAR and the Global Fund.
Gaps in Comprehensive HIV Prevention and Service Delivery
Behavioral, biomedical, and structural intervention gaps persist, limiting impact.
Innovative combination HIV prevention approaches are essential to reduce new infections and strengthen prevention efforts.
Threats to HIV Gains from Emergencies and Pandemics
COVID-19 highlighted vulnerabilities in public health systems and disrupted HIV services.
Emerging pandemics, emergencies, and natural disasters continue to pose risks, underscoring the need for stronger community leadership in prevention and preparedness.
Outcomes
1. Domestic Resource Mobilization for HIV and Health
General Approach:
Supports partners to map financing sources, analyze budgets, track allocations, and generate demand for efficiency and equity in resource use.
Zimbabwe:
National health budget increased from 8.3% (2018) to 12.8% (2023).
Leveraged the 3% National AIDS Trust Fund levy to institutionalize social contracting, enabling CSOs to access direct funding.
Supports drafting of the National Health Insurance Bill to embed accountability and sustainability in health financing.
Tanzania:
National health budget grew by 8.7% (2019–2024); domestic HIV funding increased from USD 60M to USD 88M.
Ministry of Health addressed human resources gaps, reducing primary care HRH gap from 70% (2023) to 49% (2025 projected).
Malawi:
Health allocations increased from 9% (2019) to 12% (2025).
CSOs lead community health financing education, enhancing accountability and transparency.
Influenced earmarking of new domestic revenues (car insurance, alcohol, tobacco taxes) for health in response to USG funding disruptions.
2. Official Development Assistance (ODA)
General Approach:
Positions civil society as credible, influential actors in ODA, particularly with PEPFAR and the Global Fund.
Global Fund:
Strengthened civil society influence across three NFM cycles (2017–2024), shaping USD 4.41B in investments.
Spearheaded GF CSO Charter, mentored CSO representatives in CCMs and TWGs.
Served as Technical Assistance partner for Anglophone Africa, ensuring community priorities inform funding requests.
Supported CSOs to navigate funding deallocations and safeguard community-led services.
Partners influence GC8 replenishment priorities, disease split negotiations, and catalytic funding for domestic resource mobilization.
PEPFAR:
Led civil society engagement in seven COP cycles (2018–2024) across three countries, influencing USD 4.895B in investments.
Communities achieved critical wins in HIV prevention, treatment, care, and support via People’s COPs.
Mentors CSOs to use community-led monitoring data for accountability and responsive investments.
3. Policy and Legislation for HIV and Health
Zimbabwe:
CCM amended guidelines to establish a dedicated Youth seat (2024).
Child Protection Act (2022) amended to criminalize guardians who block child access to health services.
Medical Services Amendment Bill (2024) reduced age restrictions for accessing SRH services.
Malawi:
Policy amendments strengthened supply chain management and addressed drug stockouts.
Key frameworks: National Health Strategic Plan III (2023–2030) and Master Supply Chain Transformation Plan (2021–2026).
Tanzania:
Revised National Health Multi-Sectoral SOPs for AYP Programming to include adolescents and young people living/working on the streets.
Endorsed KVP Violence Prevention Framework.
4. Differentiated Service Delivery (DSD), HIV Prevention & Access
Zimbabwe:
Secured inclusion of Community model of care in AHD Scale-up Plan; coverage expanded from 39% to 70% (2021–2024).
Led community engagement to ensure equitable access to long-acting HIV technologies: oral PrEP, Dapivirine Vaginal Ring (DVR), Cabotegravir Long-Acting (Cab LA).
Piloted and scaled innovative DSD models: OFCAD, PrEP Squad, CARGS.
Advocated for harm reduction services, ensuring community perspectives shape national HIV prevention strategies.
Monitoring and Learning
Coalition uses evidence, data and analytics to shape advocacy and track progress.
Monitoring, Evaluation, Results & Learning (MERL) hub hosted by Pangaea Zimbabwe.
Strategic innovation with “business unusual” approaches and focus on transitioning to African leadership and grant‑making
Resources





